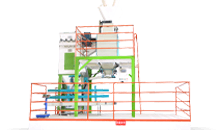
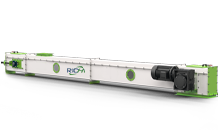
Feed mill equipment concerns all machines for the modern animal feed mill – equipment for conveying, cleaning, proportioning, grinding, mixing, pelleting, extrusion, cooling, screening, packaging and much more for feed production.
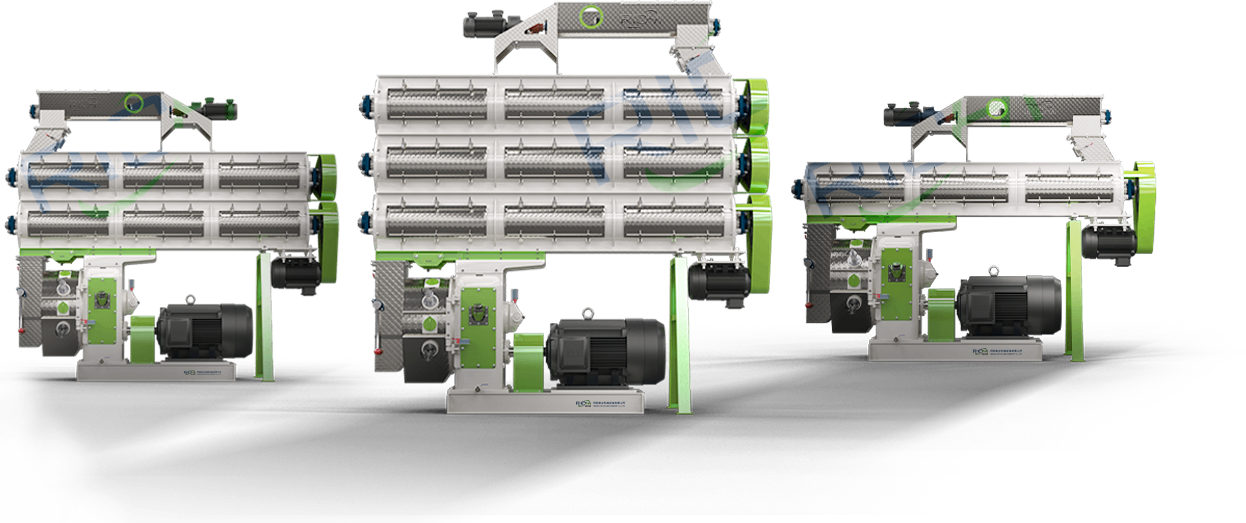
FEED MILL EQUIPMENT
Feed mill equipment are core of feed mill design and construction. Technical solutions and value-added services from Richi Machinery can reduce costs, improve quality, and create value for feed mills, farms and animal / aqua feed manufacturers.
APPLY
In RICHI we develop feed mill equipment adapted to the needs of the most demanding feed companies. RICHI’s great variety of equipment applies to both cattle, chicken, pig, premix, fish, shrimp, sheep, dog, duck, rabbit, horse and other poultry livestock aqua pet ruminant feed production.

Poultry feed production

ruminant feed production

livestock feed production

Aqua & Pet food production
cORE EQUIPMENT
RICHI designs and manufactures high-performance feed pellet mills and extruders to meet diverse nutritional requirements. These core feed mill equipment ensures optimal pellet quality, energy efficiency, and adaptability to raw material variations—key to sustainable feed production.

Hardened stainless steel ring die ensures uniform pellet density and extended service life (10,000+ hours).

Industrial-grade motors with protection deliver reliable power while reducing energy costs by 15-20%

Engineered for Excellence
At RICHI, our ring die pellet mills redefine feed production efficiency. Built with high-grade alloy steel dies and precision gearboxes, they deliver high pellet durability, low energy consumption, and 24/7 continuous operation.
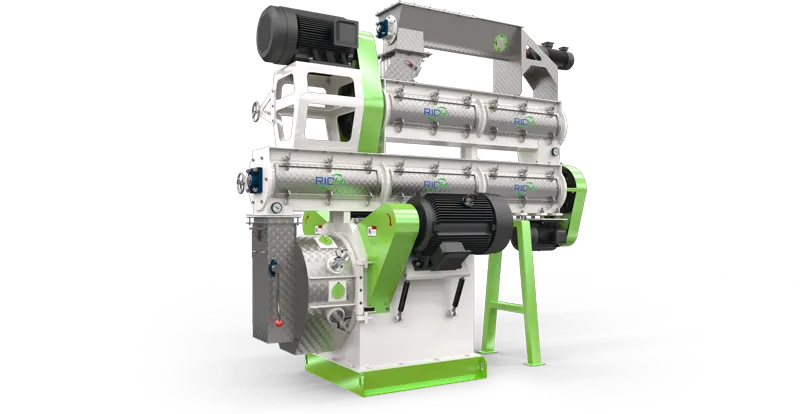

ruminant feed pellet machine

Aqua feed pellet machine

wet type extruder machine
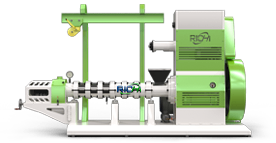
dry type extruder machine
Tailored Equipment for Optimal Animal Nutrition
From poultry to aquaculture, RICHI provides species-specific feed milling systems that enhance digestibility, hygiene, and operational efficiency. Whether producing poultry, livestock, or aqua feed, RICHI pellet mills and feed extruders ensure consistent pellet quality and minimal maintenance downtime.
Precision Performance for Every Scale
SZLH250
Capacity: 1.0-1.5 T/H
Compact yet powerful, the SZLH250 is ideal for small farms and startups, delivering 1.0-1.5 T/H of high-quality pellets with minimal energy use. Perfect for various feed processing.
SZLH320
Capacity: 3-4 T/H
Designed for mid-sized operations, the SZLH320 offers 3-4 T/H capacity, ensuring efficient pelleting for livestock and aquaculture feeds with low maintenance costs.
SZLH350
Capacity: 5-6 T/H
A workhorse for medium-scale feed mills, the SZLH350 produces 5-6 T/H of uniform pellets, optimized for ruminant and poultry diets with superior pellet durability.
SZLH420
Capacity: 10-12 T/H
The SZLH420 is a high-efficiency solution for growing feed plants, delivering 10-12 T/H with advanced conditioning for improved digestibility in cattle and swine feeds.
SZLH508
Capacity: 15-16 T/H
Built for large commercial feed mills, the SZLH508 achieves 15-16 T/H output, featuring heavy-duty construction for continuous operation in demanding environments.
SZLH558
Capacity: 20-22 T/H
A premium industrial pellet mill, the SZLH558 produces 20-22 T/H, ideal for high-volume poultry and aqua feed with precision die and roller alignment.
SZLH678
Capacity: 30-33 T/H
Engineered for mega feed plants, the SZLH678 delivers 30-33 T/H, combining high capacity with energy efficiency for cost-effective large-scale production.
SZLH768
Capacity: 38-40 T/H
The flagship of the SZLH series, the SZLH768 is the most powerful pellet mill, offering 38-40 T/H for global feed manufacturers requiring maximum output and reliability.
Technical Specifications
Our SZLH series feed pellet mills are designed with advanced engineering to deliver high output, energy efficiency, and long-term reliability. Below are the detailed technical parameters of our SZLH series, ensuring you select the ideal machine for your feed production needs.
| Model | SZLH250 | SZLH320 | SZLH350 | SZLH420 | SZLH508 | SZLH558 | SZLH678 | SZLH768 |
| Main Motor Power (kW) | 22 | 37 | 55 | 110 | 160 | 185 | 250 | 315 |
| Die Inner Diameter (mm) | 250 | 320 | 350 | 420 | 508 | 558 | 673 | 762 |
| Finished Pellet Diameter (mm) | 2~12 | |||||||
| Output (T/H) | 1.0-1.5 | 3-4 | 5-6 | 10-12 | 15-16 | 20-22 | 30-33 | 38-40 |
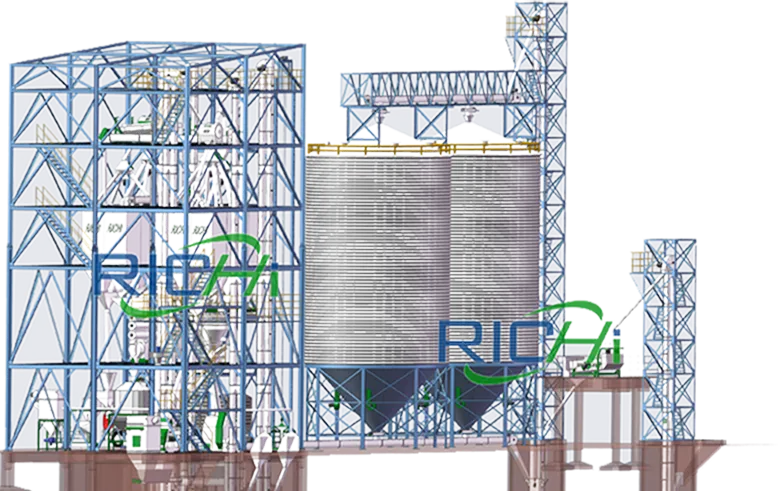
A high-efficiency animal feed mill requires more than just pelletizing and extrusion—it demands a fully integrated system for grinding, mixing, conditioning, cooling, and packaging. RICHI provides end-to-end feed mill solutions, ensuring seamless operation, optimal nutrition retention, and cost-effective production.

Key Supporting Equipment for Your Feed Mill
From raw material processing to finished feed packaging, our auxiliary systems are engineered to maximize efficiency, hygiene, and automation.
Global Success Stories
From small farms to industrial feed plants, RICHI’s feed mill equipment and solutions power successful feed production across 6 continents and 100+ countries. Our solutions are tailored to meet regional raw material availability, climate conditions, and species-specific nutritional needs, ensuring optimal performance in diverse markets. Below are highlights of our feed pellet production lines and feed processing machinery in key regions worldwide.

feed mill equipment in Africa

Our equipment in Nigeria, Kenya, and South Africa, etc., is built for high temperatures and power fluctuations, using robust hammer mills, mixers, and pelletizers to process sorghum, cassava, and local forage crops.

feed mill equipment in Europe

From Germany to Spain, our feed mill equipment meets EU feed safety regulations, with advanced conditioning, pelleting, and coating systems for swine, dairy, and aquaculture sectors.

feed mill equipment in North America
Our equipment supports poultry, cattle, and aquaculture farms and feed mills across the U.S. Canada, Mexico delivering high-capacity pellet mills, extruders, and automated feed systems.

feed mill equipment in Asia

In China, India, Vietnam, and Indonesia, our feed processing machinery supports small farms to mega feed mills, widely used in shrimp, poultry, and pig feed production.

feed mill equipment in South America

In Brazil, Argentina, Ecuador and Chile, etc., our feed mill machinery handles soybean meal, corn, and local byproducts, optimizing feed formulations for beef, poultry, and tilapia farms.

feed mill equipment in Oceania

In Australia and New Zealand, our feed pellet production lines serve dairy, sheep, and aquaculture industries, with high-output pellet mills and precise nutrient retention systems for premium feed exports.

feed mill equipment in CIS

From Russia to Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan, our equipment handles wheat, barley, and sunflower meal, providing cold-resistant and high-capacity feed systems for feed mills and farms.
By Output Capacity – Tailored for Your Scale
From 1 T/H starter plants to 160 T/H industrial systems, we engineer feed lines that grow with your business. Our modular designs ensure you pay only for the capacity you need today—with built-in flexibility for tomorrow’s expansion.

By Animal Type – Precision-Engineered Nutrition
Poultry, swine, aquaculture or specialty species—each receives optimized processing. Our species-specific systems account for unique nutritional requirements, pellet structures, and digestibility needs from raw material to finished feed.
60000 +
Backed by a 60,000 m² advanced production complex
140 +
Global footprint extends across 140+ international markets
2000 +
Over 2,000 successful feed production system installations
2013
RICHI MANUFACTURE
Established in 1995, RICHI MACHINERY has grown from a medium-sized enterprise to become China’s largest pellet production line manufacturer. With two major manufacturing bases spanning hundreds of thousands of square meters, we specialize in custom pellet machines and complete plant solutions, handling every production stage in-house—from R&D to delivery.
Our vertically integrated facilities (including dedicated sections for production, testing, and logistics) ensure premium quality, environmental responsibility, and operational reliability for feed, biomass, and fertilizer industries worldwide. For nearly three decades, we’ve partnered with clients to enhance productivity, minimize risks, and achieve sustainable outcomes through innovative engineering.
Zhengzhou Headquarters
R&D, global operations and strategic management converge

Jiaozuo New Production Base (2025)
Featuring automated production lines and Industry 4.0 technologies

Kaifeng Original Complex (Since 1995)
Our manufacturing legacy began and quality traditions endure
Certifications & Patents
As a world-leading feed mill equipment manufacturer, RICHI Machinery demonstrates its engineering prowess through internationally recognized certifications and proprietary innovations.
Our ISO quality management system, CE compliance, BV-certified production processes, GOST-R for Russian compliance, ATEX explosion-proof certification for EU safety standards, FDA registration for U.S. market access, and EHEDG hygienic design certification validate our commitment to global standards, while 50+ patented technologies in pellet mills, extruders and automation systems deliver unmatched performance.

When you choose RICHI, you’re selecting globally validated, future-proof solutions backed by the industry’s most comprehensive certification portfolio.

01
Consultation
Our experts provide professional advice to understand your specific feed production requirements.

02
Design
We develop customized solutions with optimized layouts and equipment configurations for your project.

03
Manufacturing
All feed mill equipment is precision-built using quality materials in our ISO-certified factories.

04
Shipping
We handle secure packaging and global logistics with reliable delivery timelines.

05
Installation
Our engineers supervise on-site assembly and commissioning for smooth operation.

06
Training
Comprehensive operator instruction ensures proper use and maintenance of equipment.

07
After-sales
Dedicated support team provides troubleshooting and technical assistance.

08
Spare Parts
Genuine components are available worldwide with fast delivery service.
FAQs – Your Feed Equipment Queries Answered
Navigating feed mill equipment selection and operations can raise important questions. Below we address the most common inquiries about our feed production solutions, from technical specifications to after-sales support. Whether you’re evaluating pellet mills, planning a new feed mill, or optimizing existing operations, these answers provide clarity to help you make informed decisions.
How to start a complete feed mill?
+
Animal & Aqua Feed Mill Technology is the process of grinding and making feed ingredients into a form that is suitable for animal and aqua consumption. The feed mill process can be divided into 7 main stages: raw material handling, grinding, mixing, pelleting/extrusion, cooling/drying, screening and packaging.
Feed milling is a critical step in the production of animal and aqua feed, as it creates a uniform mixture that meets animal nutritional requirements and is easy for animals to digest. Before embarking on the design and construction of a Feed Mill Plant, several questions will need to be answered by the customer. Below are some of the more important ones:
- Product Plan: What type of animal (poultry, pigs, cattle, goat, fish, shrimp or pets) is the feed being developed for? This will usually determine the ingredients to be processed, and the product characteristics necessary for certain animal diets.
- Raw Materials: This dictates whether the feed mill will require raw material pre-processing steps such as cleaning, size reduction, pre-conditioning etc.
- Feed Mill Scale: How much feed will the mill produce? This directly impacts the size and layout of processing equipment employed in converting raw materials into products.
- Facilities: The footprint and available head space in the facility will impact whether the feed mill plant layout uses a vertical or horizontal set-up.
- Products: What are required characteristics of the final product will impact the processing steps utilized in the feed mill? This will also determine if additional processing steps such as pressing, shaping, coating, cooling, packaging etc. will be required.
- Electricity: Available power in terms of voltage, frequency and phase, and proximity of power source to the proposed site of the feed mill.
- Water and Steam: The quality and amount of water and steam to be made readily available at the site will depend on several factors.
01
What are the prices for feed mill equipment of different capacities?
+
Here are the investment costs for a complete set of feed mill equipment for different capacities:
| Production Scale | Total Power | Project Site Requirements | Production cycle | Installation cycle | Investment Cost(USD) |
| 1-2T/H | 47-75KW | 300-500m² | 20 Days | 7-15 Days | 10,000-50,000 |
| 3-4T/H | 53-165KW | 300-700m² | 20 Days | 15-20Days | 50,000-120,000 |
| 5-7T/H | 68-259KW | 400-800m² | 20-30 Days | 20-40Days | 70,000-250,000 |
| 8-10T/H | 125-410KW | 800-2000m² | 30-40 Days | 45-60 Days | 150,000-300,000 |
| 12-20T/H | 358-620KW | 1500-3000m² | 40-50 Days | 60-90 Days | 250,000-580,000 |
| 25-40T/H | 545-870KW | 2000-4000m² | 50-60 Days | 90-120Days | 450,000-850,000 |
| 50-60T/H | 710-1120KW | 3000-5000m² | 60-70 Days | 100-140 Days | 900,000-1,400,000 |
| 60-80T/H | 815-1370KW | 5000-8000m² | 70-90 Days | 130-160 Days | 1,450,000-1,800,000 |
| 80-100T/H | 1230-1700KW | 8000-20000m² | 90-120 Days | 160 -190Days | 2,000,000-3,000,000 |
02
How to Choose the Right Feed Mill Equipment?
+
Selecting feed mill equipment requires a holistic approach that considers multiple operational and environmental factors. As an industry leader with decades of hands-on experience, we break down the key decision-making dimensions you should evaluate:
1. Production Scale & Growth Plans
- Small farms (1-5 T/H): Compact, modular systems with manual controls offer cost-effective solutions
- Mid-sized operations (5-20 T/H): Semi-automated lines with recipe memory functions
- Large feed mills (20+ T/H): Fully automated plants with smart monitoring systems
*Always account for 3-5 year capacity projections – retrofitting is 30% more expensive than proper upfront sizing*
2. Feed Type & Animal Nutrition Requirements
- Poultry: High-speed pelleting for crumble feeds with strict pellet durability standards
- Ruminants: Heavy-duty equipment for high-fiber formulations (12-18% crude fiber)
- Aqua feed: Low-temperature extrusion systems for floating/sinking requirements
- Pet food: Precise coating systems for fat retention and palatability
3. Raw Material Profiles & Formula Complexity
- Grain-heavy diets: Require robust grinding systems (hammer mill screen ≤2mm)
- High-oil formulas: Need specialized conditioning (triple-pass steam jackets)
- Micro ingredients: Demand precision dosing systems (±0.1% accuracy)
Pro Tip: Always test your local ingredients – moisture/variability impacts equipment selection
4. Facility Layout & Spatial Constraints
- Vertical designs (limited footprint): Bucket elevators and tower-type arrangements
- Horizontal layouts: Pneumatic conveying with centralized control points
- Retrofits: Modular equipment with flexible connection points
5. Regional Regulations & Compliance
- EU markets: Require ATEX certification for dust explosion protection
- US operations: Need FDA-compliant material contact surfaces
- Tropical climates: Equipment rated for 90% humidity operation
6. Energy Infrastructure Realities
- Unstable power grids: Machines with soft-start systems and backup drive options
- High electricity costs: Energy recovery systems (heat exchangers on dryers)
- Off-grid locations: Diesel-driven options with 10-15% higher throughput buffers
7. Labor Skill Levels
- Highly trained staff: Fully automated systems with HMI interfaces
- Entry-level operators: Simplified controls with fault diagnosis indicators
- Remote locations: Equipment with IoT-enabled remote troubleshooting
The RICHI Difference
We don’t just sell machines – we conduct Site-Specific Suitability Audits that examine:
✓ Raw material lab analysis
✓ Power quality testing
✓ Local climate stress factors
✓ Regulatory compliance mapping
This approach helped a Kenyan client avoid £120,000 in unnecessary equipment by right-sizing their system to actual maize quality rather than European standard assumptions.
03
What types, sizes, and forms of feed can your feed mill equipment process?
+
At RICHI Machinery, our feed equipment solutions are engineered to handle the full spectrum of modern feed production requirements. Here’s how we address various processing dimensions with technical precision:
1. By Feed Physical Form
(1) Pellets:
- Diameter range: 1.0-12mm (standard)
- Special sizes: 0.8mm micro-pellets for fry feed
- Custom shapes: Bone, fish, star geometries for branding
(2) Crumbles:
- Precision grading from 0.5-2.5mm
- Uniform particle distribution (CV<15%)
(3) Mash Feeds:
- Particle size control: 200-2000μm
- Homogeneity: >95% mixing uniformity
(4) Extruded Feeds:
- Floating: 80-95% buoyancy
- Sinking: Controlled density (1.2-1.4g/cm³)
2. By Animal Nutrition Requirements
(1) Poultry:
- Broilers: 2-3mm durable pellets
- Layers: 3-4mm high-calcium formulations
- Duck: 3-5mm water-resistant pellets
(2) Aquatic Species:
- Shrimp: 1.0-2.5mm slow-sinking
- Fish: 2-8mm floating/sinking options
- Crab: Special high-stability pellets
(3) Ruminants:
- Cattle: 6-12mm high-fiber pellets
- Sheep: 4-8mm protein-enriched
- Dairy: TMR mixtures with precise chop length
3. By Raw Material Characteristics
(1) Cereals-Dominant:
- Corn/soy: Standard pelleting (3-5% moisture addition)
- Wheat/barley: Pre-conditioning requirements
(2) Alternative Proteins:
- Insect meal: Low-temperature processing
- Single-cell protein: Special binding solutions
(3) High-Fiber Ingredients:
- Rice bran: Die design adaptations
- DDGS: Moisture control systems
4. Specialized Applications
(1) Pet Food:
- Kibble sizes: 5-15mm
- Shape variations for dental health
(2) Functional Feeds:
- Probiotic: Temperature-controlled processing
- Medicated: Coating systems
04
How do I choose the core feed mill equipment—feed mill pellet machine?
+
When choosing a ring die pellet mill for your feed production, these are the key factors to consider:
1. Production Requirements
- Match the feed mill’s capacity to your daily production needs with 20% overhead
- Consider future expansion plans when selecting size
- Verify throughput claims with actual feed formulas, not just test runs
2. Feed Type Compatibility
- For poultry feeds: Look for quick die-change systems
- For ruminant feeds: Ensure adequate compression zone length
- For aqua feeds: Confirm corrosion-resistant materials
- Avoid for floating feeds (requires extruder)
3. Structural Evaluation
- Inspect frame construction: Solid cast beats welded assemblies
- Check bearing sizes: Larger lasts longer under heavy loads
- Examine drive train: Gearboxes should have serviceable components
4. Design Features
- Look for adjustable roller gap systems
- Prefer self-lubricating bearings over manual grease points
- Ensure easy access for routine maintenance
5. Material Quality
- Dies should be made from certified alloy steels
- Rollers require hardened surfaces
- Contact surfaces should use food-grade materials
6. Manufacturing Standards
- Ask about in-process quality checks
- Request evidence of performance testing
- Verify assembly precision levels
7. Reliability Indicators
- Review maintenance schedules from existing users
- Compare warranty terms between suppliers
- Check spare parts availability in your region
8. Manufacturer Qualifications
- Minimum 10 years specialized experience
- Look for project references in similar applications
- Verify relevant industry certifications
Practical Selection Tips:
- Always test with your actual feed formulas
- Compare energy consumption at your target production rate
- Evaluate service support before purchasing
- Consider total cost of ownership, not just price
For the most accurate assessment, arrange to visit an operating installation using similar formulas to yours. Observe:
- Ease of operation
- Routine maintenance procedures
- Pellet quality consistency
Remember that the best pellet mill is the one that reliably produces quality feed with minimal downtime in your specific operating conditions.
05
How to choose feed mill equipment—a feed mixer machine?
+
Choosing the optimal feed mill mixer requires careful evaluation across several critical dimensions:
1. Batch Size Requirements
- Calculate based on your pelleting/extrusion line capacity
- Allow 10-15% extra capacity for formula changes
- Consider peak production demands, not just averages
2. Mixing Performance
- Look for CV (coefficient of variation) ≤5% for micro ingredients
- Verify mixing uniformity test results with similar formulas
- Check dead zones in mixing chamber design
3. Material Compatibility
- For high-oil formulas: Require liquid dispersion systems
- For fibrous materials: Ensure proper ribbon/plough design
- For abrasive minerals: Check wear protection measures
4. Structural Evaluation
- Inspect shaft and bearing assembly robustness
- Check access doors for proper sealing
- Evaluate discharge mechanism reliability
5. Operational Features
- Prefer automated liquid addition systems
- Look for quick-clean designs
- Consider noise levels in your facility
6. Maintenance Requirements
- Compare grease intervals (500+ hours preferred)
- Check component accessibility
- Review typical spare parts consumption
Practical Selection Process:
- Formula Analysis
- List all ingredients by particle size/density
- Identify challenging components (micros, liquids)
- Note any abrasive or corrosive materials
- Performance Testing
- Conduct trial mixes with your formulas
- Take multiple samples for uniformity analysis
- Check residue levels after discharge
- Supplier Evaluation
- Request customer references with similar applications
- Verify service network in your region
- Compare warranty coverage details
Key Questions to Ask:
- What’s the actual mixing time for my formulas?
- How is liquid addition controlled?
- What maintenance is required weekly/monthly?
- How does performance change with wear?
Red Flags to Watch For:
- Suppliers unwilling to demonstrate mixing tests
- Lack of performance data from existing installations
- Vague answers about maintenance requirements
For optimal results, always test the mixer with your most challenging formula before purchasing. The right mixer should handle your current needs while allowing for future formulation flexibility.
06
How to choose feed mill equipment—feed mill grinder?
+
Choosing the right feed crusher requires careful consideration of several operational factors:
1. Raw Material Characteristics
- Grain hardness (test your local corn/wheat samples)
- Initial particle size distribution
- Moisture content range (especially for fibrous materials)
2. Required Final Particle Size
- Starter feeds: ≤1.0mm uniform grinding
- Grower/finisher: 1.5-2.5mm with controlled distribution
- Ruminant feeds: 3.0-5.0mm with fiber preservation
3. Production Capacity Needs
- Match to your batching system cycle time
- Consider peak vs. average throughput requirements
- Account for future formula expansions
4. Hammer Mill vs. Roller Mill
- Hammer mills: Better for multi-grain operations
- Roller mills: Preferred for consistent particle shaping
- Combination systems: For specialized applications
5. Critical Design Features
- Screen changing mechanism (quick-release preferred)
- Wear protection on impact surfaces
- Airflow design for temperature control
- Vibration damping systems
6. Operational Considerations
- Noise levels for your facility layout
- Dust control requirements
- Energy consumption per ton processed
- Ease of routine maintenance
7. Quality Verification Methods
- Particle size distribution analysis
- Temperature rise monitoring
- Production rate consistency testing
- Residual accumulation checks
Practical Selection Process:
- Material Testing
- Conduct trial runs with your actual ingredients
- Measure particle size distribution curves
- Monitor temperature changes during grinding
- Performance Evaluation
- Verify throughput claims with your formulas
- Check power consumption under load
- Assess ease of screen changes
- Supplier Assessment
- Request customer references with similar materials
- Review service network availability
- Compare warranty coverage details
Key Questions to Ask Suppliers:
- What’s the expected wear part life with my materials?
- How is particle size consistency maintained?
- What maintenance is required daily/weekly?
- How does performance change with screen wear?
Important Red Flags:
- No demonstration equipment available
- Unwillingness to test your materials
- Vague answers about power consumption
- Lack of particle size distribution data
For optimal results, always test the crusher with your most challenging ingredients before purchasing. The right machine should deliver consistent particle size while minimizing fines generation and energy use.
07
How to choose feed mill equipment —— feed extruder machine?
+
When evaluating feed extruders for your operation, focus on these critical aspects:
1. Application-Specific Selection
• Aquatic feeds:
- Twin-screw for superior floating/sinking control
- Precise thermal management for starch gelatinization
• Pet foods:
- High-shear configurations for kibble texture
- Versatile die options for shape variety
• Expanded livestock feeds:
- Dry-type systems for cost efficiency
- Moderate shear for nutrient preservation
2. Throughput Requirements
- Match extruder size to your pelleting line capacity
- Account for 15-20% formula variation impact
- Consider future product development needs
3. Process Control Capabilities
- Look for:
Independent zone temperature controls
Variable screw speed adjustment
Precise moisture monitoring
Automated throughput regulation
4. Component Durability
- Screws and barrels should feature:
Wear-resistant alloys
Modular design for partial replacement
Proper hardening treatments
5. Operational Efficiency
- Evaluate:
Steam consumption rates
Specific mechanical energy (SME)
Downstream drying requirements
Changeover time between formulas
6. Maintenance Considerations
- Preferred features:
Quick-release die assemblies
Accessible wear part replacement
Self-cleaning elements
Corrosion-resistant construction
Implementation Strategy:
- Formula Analysis
- Test your recipes on pilot equipment
- Document optimal processing parameters
- Identify any special requirements
- Facility Assessment
- Verify utility capacities (steam, power)
- Plan for ancillary equipment needs
- Consider material flow logistics
- Supplier Evaluation
- Request:
Performance guarantees
Customer references
Service response commitments
Spare parts availability
Critical Questions:
- What’s the expected production variance with my formulas?
- How is product density controlled?
- What’s the typical wear part replacement schedule?
- How does the system handle formula transitions?
Performance Verification:
- Insist on:
Trial runs with your materials
Complete parameter documentation
Energy consumption measurements
Product quality testing
The right extruder should deliver consistent product quality while adapting to your specific production requirements and future growth plans. Always verify performance claims with actual testing under your operating conditions.
08
Do you offer fully automated feed packaging and palletizing systems ?
+
Yes, we provide fully automated packaging and palletizing systems tailored to your specific production needs. Our solutions cover everything from precision weighing to stacking and logistics integration, designed to handle diverse packaging requirements across multiple industries.
Key Features of Our Systems:
- Multi-Format Packaging: From 5kg to 50kg bags, including woven PP, paper, and biodegradable options
- High-Speed Weighing: Dynamic checkweighers ensure ±0.1% accuracy
- Robotic Palletizing: 6-axis robots with custom end-effectors for stable stacking
- Industry Adaptability: Configured for feed, pet food, premixes, and specialty powders
Why Choose Our Automated Packaging Systems?
✔ Seamless Integration – Connects with existing pellet/cooling lines
✔ Reduced Labor Costs – Full automation minimizes manual handling
✔ Traceability – Barcode/QR code printing for batch tracking
✔ Durability – Stainless steel contact points for abrasive materials
Beyond Feed Mills:
Our systems are deployed in:
- Pet Food – Precise kibble portioning
- Aqua Feed – Moisture-resistant bagging
- Premix & Additives – Dust-tight filling
- Biomass Pellets – Heavy-duty bag handling
Next Steps:
Request a Packaging Line Audit – we’ll analyze your:
→ Current bagging bottlenecks
→ Required throughput (bags/hour)
→ Future expansion plans
09
Do you provide complete feed mill equipment system process design and layout?
+
Yes, we deliver complete feed mill solutions, handling every stage from initial process design to final production startup. Our team specializes in creating optimized feed mill equipment layouts that maximize efficiency while minimizing operational costs.
Our End-to-End Project Approach:
- Process Engineering
- Customized feed mill equipment configurations based on your:
→ Raw material profiles
→ Target feed types (pellets, crumbles, mash)
→ Daily throughput requirements
- Facility Layout Optimization
- 3D modeling for:
→ Material flow efficiency
→ Future expansion space planning
→ Utility distribution (power, air, steam)
- Turnkey Implementation
- Single-source responsibility for:
→ Feed mill equipment manufacturing
→ Structural steel and platform engineering
→ Dust control and safety systems
Why Clients Choose Our Design Services:
✔ No Hidden Gaps – We address electrical, automation and HVAC needs alongside core feed mill equipment
✔ Regulatory Compliance – Designs meet EU, FDA, and local safety standards
✔ Throughput Validation – Guaranteed production capacities based on your formulas
10